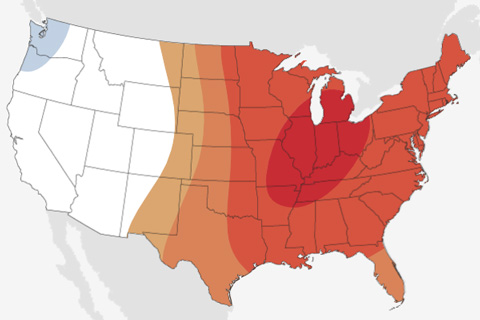
It's the start of meteorological spring, and warmer-than-average temperatures are favored for the central/eastern United States, while the precipitation outlook is more variable.
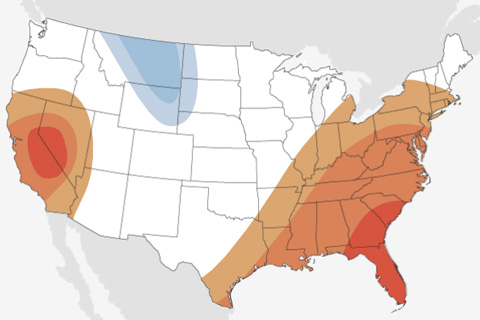
Across a wide swath of the United States from the Gulf Coast to the Mid-Atlantic, February is more likely to be above average than below average in terms of both temperature and precipitation.
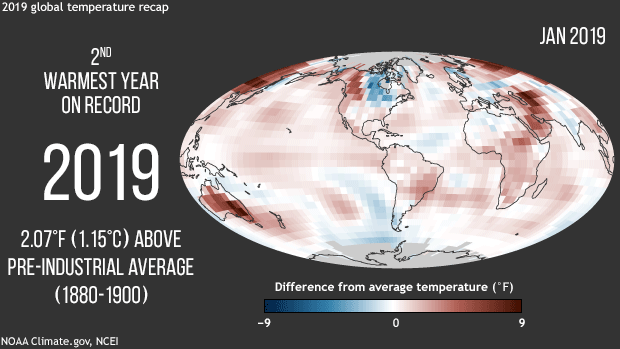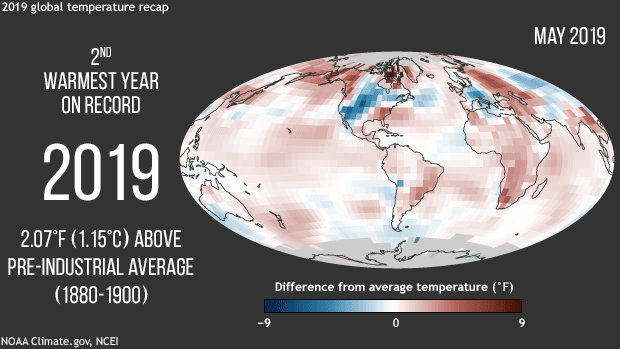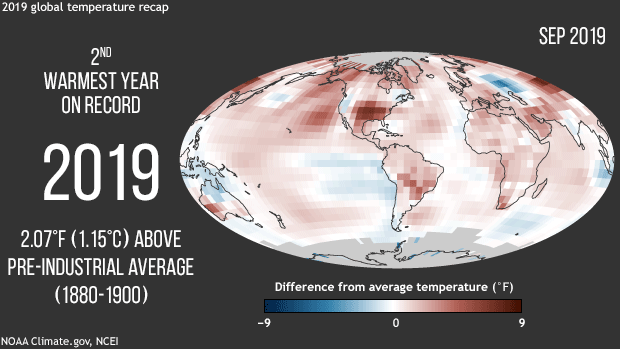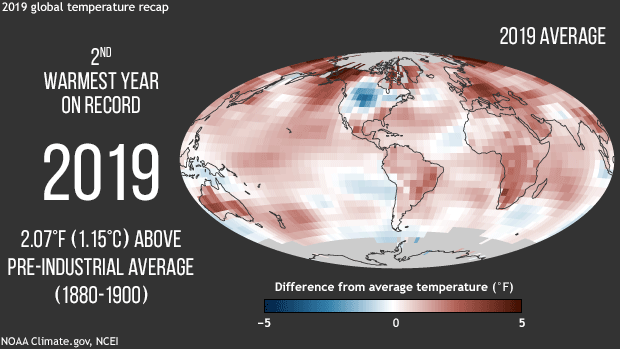
NOAA, NASA scientists confirm Earth’s long-term warming trend continues. The average surface temperature was more than 2 degrees (F) above pre-industrial conditions.

Under high pressure and sunny skies, roughly 95 percent of the surface experienced melting at some point in the summer, well above the 1981-2010 average of about 64 percent, equivalent to the previous record set in 2012.
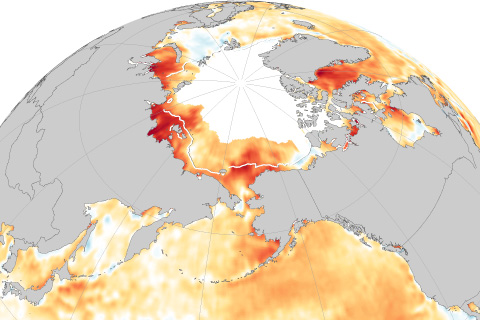
With few exceptions, unusual warmth dominated Arctic Ocean basins in 2019.
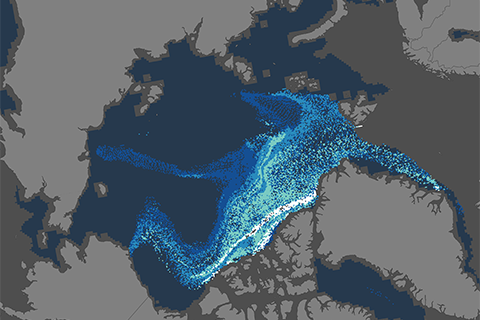
In March 1985, sea ice at least four years old made up 33 percent of the ice pack in the Arctic Ocean; in March 2019, ice that old made up 1.2 percent of the pack.
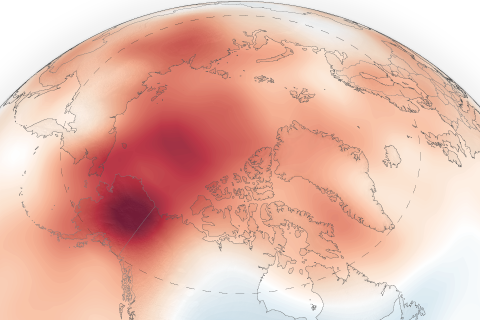
In 2019, air temperatures over the Arctic were the second-warmest on record, continuing a string of 6 years that have been warmer than all other periods in the historic record dating back to 1900.
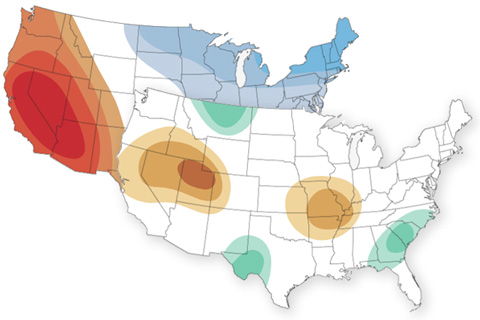
NOAA National Weather Service's Climate Prediction Center released their temperature and precipitation outlook for November. What does it say? Read on to find out.
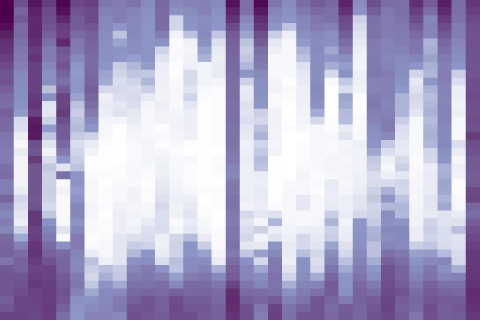
Weather balloons launched at the South Pole each spring routinely find areas of the Antarctic stratosphere where ozone has been completely destroyed. In 2019, they found no such areas.
