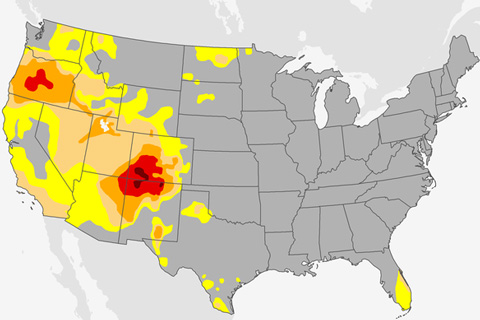
Stubborn drought affected the U.S. Southwest and Four Corners region throughout 2018, stressing water supplies, agriculture, and natural ecosystems.
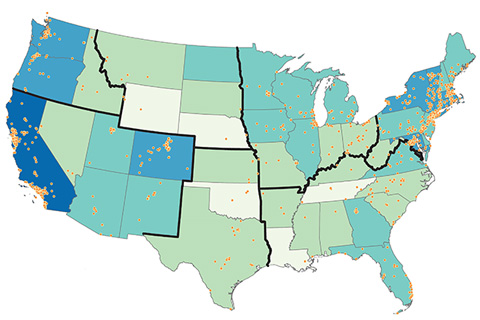
Cities and states across the U.S. already engage in emission mitigation activities. Continuing to reduce emissions will save thousands of lives and billions of dollars.
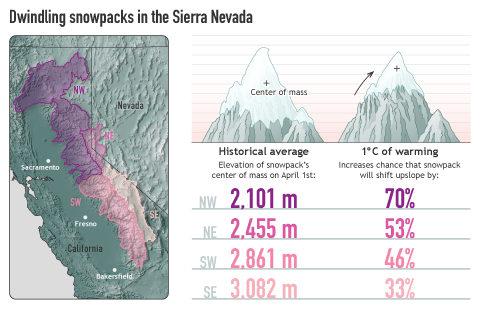
A 1°C (1.8°F) increase in average winter air temperature will have a significant impact on Sierra Nevada snowpack, but different parts of the mountain range will respond differently.
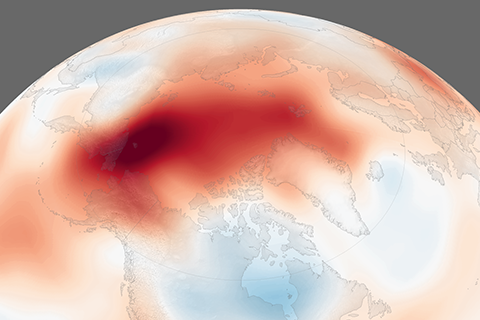
September 2018 was the second-highest on record, and all five years since 2014 have been warmer than any prior records.
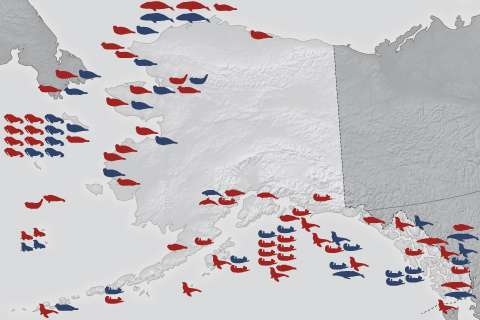
As oceans warm, harmful algal blooms move northward into regions where populations have little or no prior exposure.
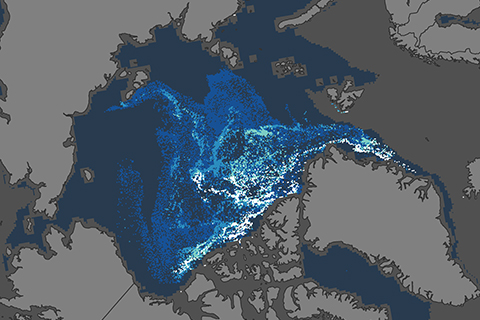
Unlike the rest of us, Arctic sea ice is younger and thinner than it was in the mid-1980s.
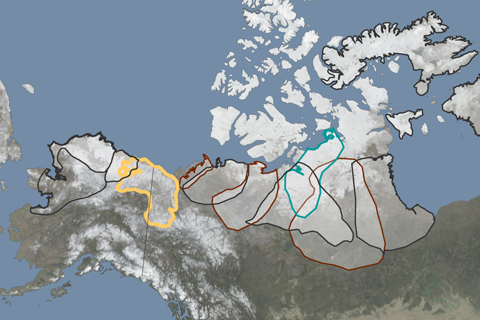
Reindeer and caribou abundance has declined 56 percent over the past two decades.
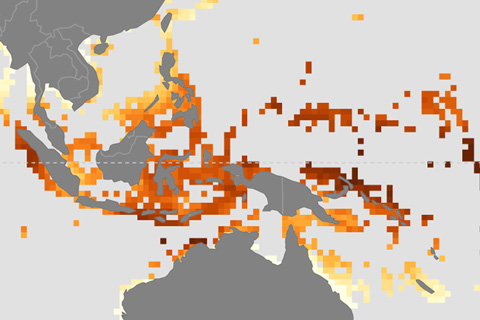
Corals reefs face double threats from rising atmospheric carbon dioxide: severe heat stress and ocean acidification. NOAA researchers have produced maps of future changes in both threats to allow managers to identify the most vulnerable reefs.
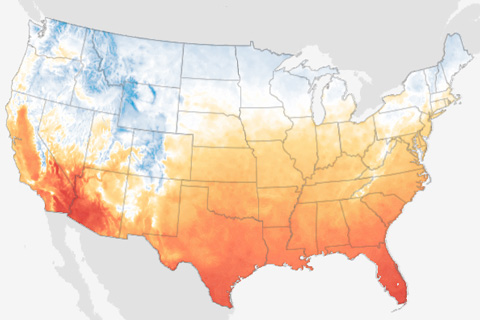
This animated gif shows how October average temperatures in the contiguous United States are projected to change in coming decades if global carbon dioxide emissions continue along a high-emissions pathway.
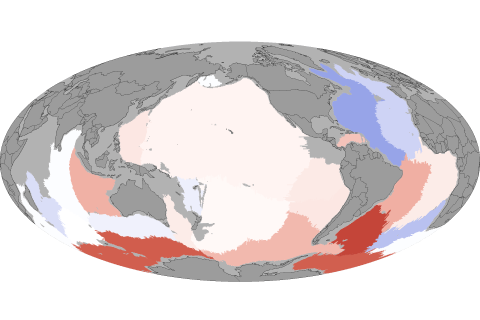
Earth's coldest waters are warming, an indication that global warming has reached one of the most remote corners of the ocean's circulatory system.