Great Lakes ice cover affects activities ranging from shipping to recreation. Accurate forecasts are critical, but forecast products have been spatially and temporally limited. The next generation of NOAA’s Great Lakes Operational Forecast System (GLOFS) aims to fill information gaps.
The chances that La Niña will last through summer are only slightly higher than the chances of a short dip into neutral before returning to La Niña by early winter. How will it affect the hurricane season?
Summer-like heat felt across much of the South during May. Drought conditions improve for some, yet remain across much of the West.
Prior to the Industrial Revolution, CO2 levels were consistently around 280 ppm for almost 6,000 years of human civilization. Carbon dioxide measured at NOAA’s Mauna Loa Atmospheric Baseline Observatory reached 421 parts per million in May 2022.
Most models project that further warming will decrease the total number of Atlantic hurricanes, but increase the number of very strong storms.
Western Water Assessment has recently improved and updated its High-Impact Weather and Climate Events Database, a collection of significant weather and climate-related events in Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
Western Water Assessment (WWA) has just released the Utah Hazard Planning Tool, which provides resources about the historical incidence, current risk, and future projections of natural hazards in the state.
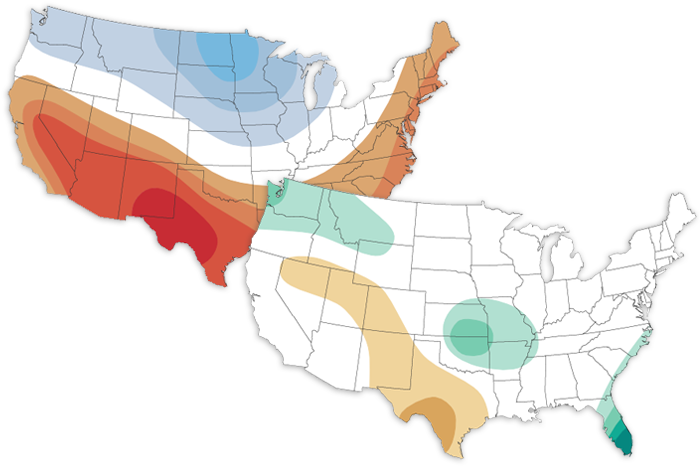
The June climate outlook favors a hotter-than-average start to summer for the southern and eastern United States and a cooler-than-average June for the north-central and northwestern U.S.
This summer’s western wildfire season is likely to be more severe than average but not as devastating as last year’s near-record, according to an experimental prediction method developed by scientists at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).