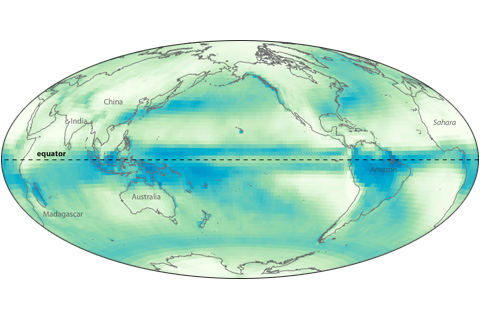
Near the Earth’s equator, solar heating is intense year round. Converging trade winds and abundant water vapor all combine to produce a persistent belt of daily showers known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
As far back as August 2010, NOAA's seasonal climate models predicted that rainfall would be heavier than normal across Indonesia and Southeast Asia in early 2011. The cause? La Niña.

On Hawaii’s Big Island, prevailing Pacific trade winds from the northeast bring more rainfall to northern & eastern slopes, leading to dramatic differences in vegetation on different sides of the island.

When the winds are right, dust from the deserts of the U.S. Southwest blows onto the snow-capped Rocky Mountains. How do dirty snowfields contribute to the loss of more than 250 billion gallons of water in the Colorado River?

At the highest point atop the Greenland Ice Sheet, Matthew Shupe and his colleagues are installing a suite of climate and weather instruments. Their goal is to better understand the role of clouds in the rapid warming observed across the Arctic region.

Two photographs, taken 18 months apart, show a significant decrease in Lake Powell during the most serious period of recent drought.

In May and June each year, speculation about the coming of the monsoon fills newspapers and conversations across India. Everyone is concerned about if, when, and how much rain will arrive. But none have more at stake than India’s over 100 million farming households.
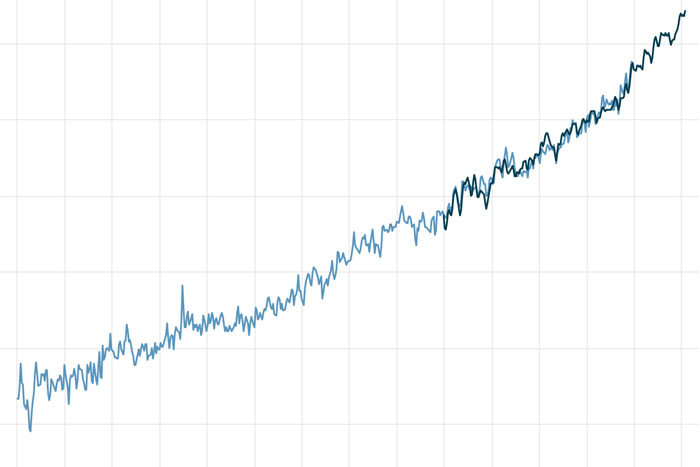
Global average sea level has risen 8-9 inches since 1880, and the rate is accelerating thanks to glacier and ice sheet melt.
The yearly precipitation across the Arctic has increased more than 10 percent since 1951, with winter experiencing the largest seasonal increase.
Heat-driven drying is playing a larger role than low precipitation in 21st-century Western droughts.