Differences in exposure to sunlight, cloud cover, atmospheric circulation patterns, and other factors influence whether and how much a location is warming or cooling.
Thanks to the global oceans, Earth's surface temperature doesn't react instantly to the full impact of a climate disturbance. That delayed reaction has pros and cons.
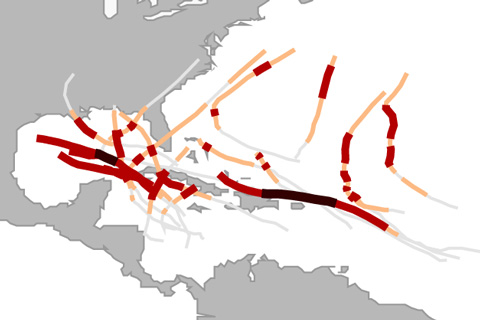
Pulled from the Fourth National Climate Assessment report published in November 2018, this FAQ explains what we know about the connection between global warming and Atlantic hurricanes.
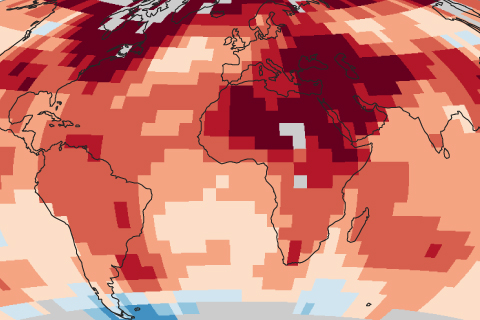
The 15 years from 1998–2012 were the warmest on record at that time, but the rate of global surface warming was slower than it had been in the 2-3 decades prior thanks to several natural influences. Meanwhile, the ocean's heating imbalance continued to climb.

El calentamiento global es un síntoma del problema mucho más grande del cambio climático causado por los humanos.

Las actividades humanas emiten 60 veces o más la cantidad de dióxido de carbono liberado por los volcanes cada año.

Human activities emit 60 or more times the amount of carbon dioxide released by volcanoes each year.

Global warming is one symptom of the much larger problem of human-caused climate change.
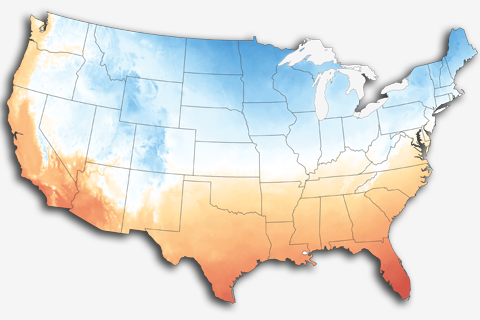
The United States has plenty of warming wiggle room before it gets too warm to snow, and a wetter atmosphere may boost snow totals for some storms.
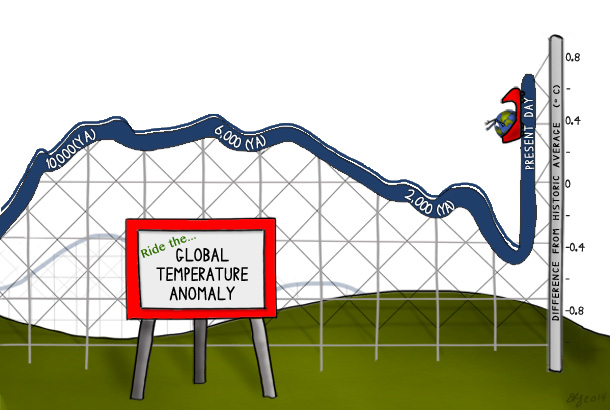
Natural variability can explain much of Earth's average temperature variation since the end of the last ice age, but over the past century, global average temperature has risen from near the coldest to the warmest levels in the past 11,300 years.